In the midst of the challenges facing the B-segment car market from new energy vehicles and the stable dominance of Japanese and German brands, the new Mondeo is poised to redefine the value system of traditional gasoline vehicles with a combination of "gasoline car prices and electric vehicle intelligence".
The new Changan Ford Mondeo was officially launched recently, with prices ranging from 149,800 to 199,800 yuan. Along with the price announcement, the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8155 chip and the new generation SYNC+ intelligent connectivity system were also announced as standard across the entire range.

The pricing strategy of the new Mondeo can be described as aggressive.
With a starting price of 149,800 yuan, it not only falls below the entry-level price of mainstream joint venture B-segment cars, but even touches on the price range of some A+ segment compact sedans. And this price isn't just a gimmick. Even the 1.5T Fashion model at 149,800 yuan comes standard with basic features such as automatic LED headlights, an electric sunroof, a 13.2-inch touchscreen, and the SYNC+ intelligent connectivity system.

As a facelift model, the most significant intelligent upgrade for the Mondeo is that it comes standard across the entire range. Official data shows that the new generation SYNC+ system is equipped with a Qualcomm Snapdragon 8155 chip, achieving a response speed of "operable immediately upon power-on, with voice interaction in 2 seconds." For traditional joint venture brands that have long been criticized by users for their "outdated in-car systems," this practice of directly equipping top-tier intelligent hardware as standard equipment breaks industry norms.

The upgraded powertrain is another key selling point of the new Mondeo. It features a fifth-generation 2.0T EcoBoost engine, with maximum power increased to 192 kW (approximately 261 hp) and peak torque reaching 408 Nm. Compared to the previous model, this represents a 7 hp increase and a 15 Nm increase in torque, and it can use 92-octane gasoline, reducing daily operating costs while maintaining Ford's consistent performance advantage.

The exterior design changes aren't radical, but they make the new car look more refined. The new Mondeo abandons the previous split headlights, adopting a new integrated design with three horizontally arranged daytime running light strips forming a striking visual feature. At the rear, the taillight structure has been adjusted, incorporating the classic "three-pillar" element that pays homage to Ford's performance car series. The body dimensions remain unchanged, with a length, width, and height of 4935/1875/1500 mm and a wheelbase of 2945 mm, placing it among the larger mid-size cars.

The interior design continues the current model's technological style, with the 1.1-meter-long 27-inch 4K full-screen display remaining the visual focus of the cabin. Practical details have been improved, with the center console area redesigned as a floating design, and the addition of a wireless charging pad for mobile phones and open cup holders, enhancing space utilization.
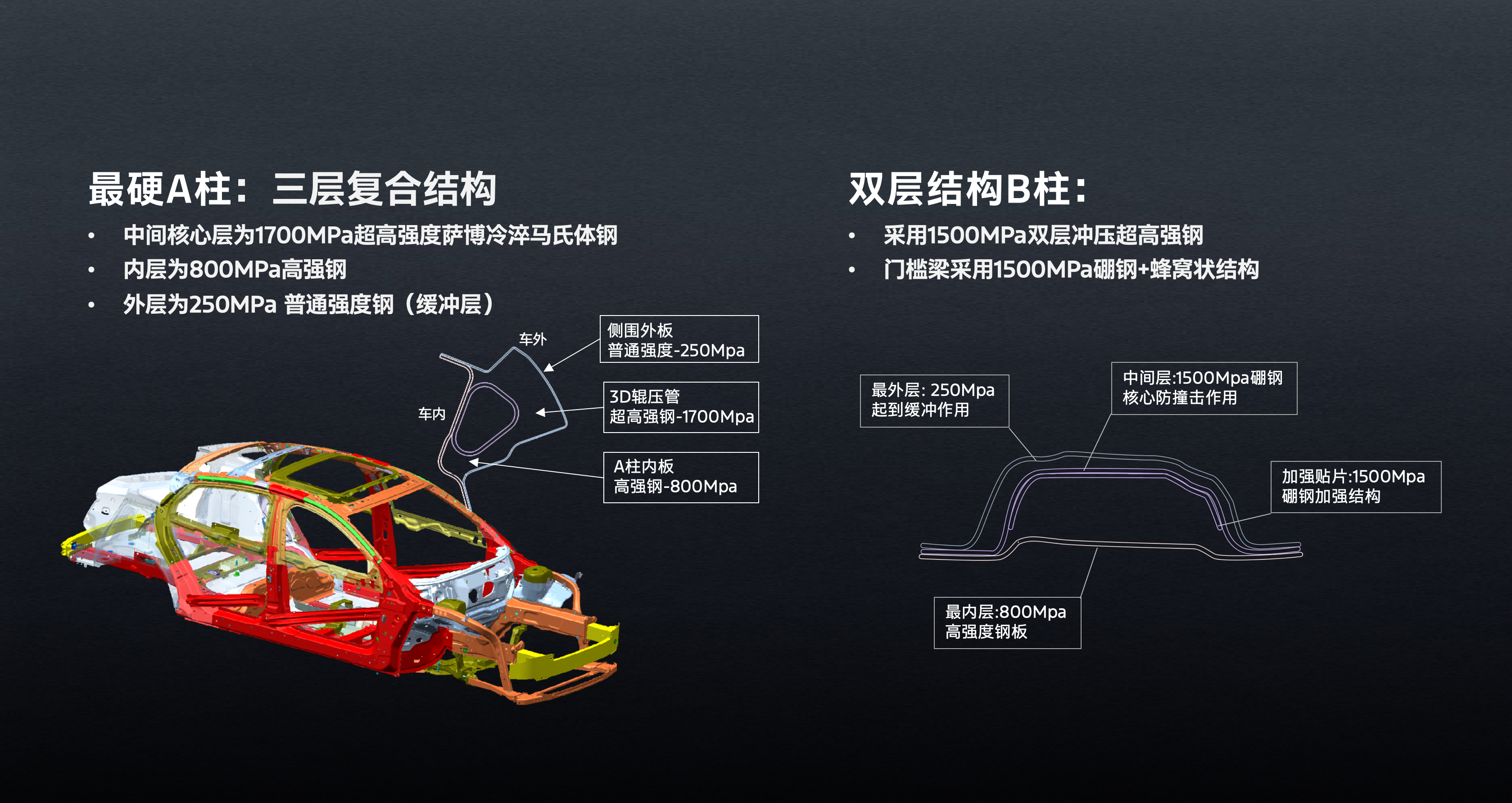
In terms of safety, the new Mondeo continues Ford's commitment to safety, adopting a super-strong cage-type body with a comprehensively reinforced body structure. The proportion of high-strength steel with a strength of 600MPa or higher has been increased to 53%. In terms of active safety, it is equipped with the Co-Pilot 360™ driver assistance system, which includes multiple active safety functions such as ACC full-speed adaptive cruise control and PCA collision avoidance assist, providing users with all-round safety protection.

The significance of this facelift of the new Mondeo transcends a mere model upgrade. It provides a reference for traditional automakers anxious about electrification: instead of rushing into full electrification, they can revitalize their products by injecting cutting-edge intelligent technologies into mature gasoline vehicle platforms. This path of "deeply intelligent gasoline vehicles" offers a pragmatic option for traditional brands with limited resources or slower pace in their electrification transformation.


